With
nouns such as /sáikál/ ‘cycle’, /m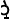 t t r/
‘motor’, /thù r/
‘motor’, /thù ná/
‘chair’, /d ná/
‘chair’, /d kán/
‘table’, /và:n/ ‘sky’, /àràsí/ ‘star’, /nísá/ ‘sun’
the post-position /cù/ is preferred. kán/
‘table’, /và:n/ ‘sky’, /àràsí/ ‘star’, /nísá/ ‘sun’
the post-position /cù/ is preferred.
/pùm/ |
| Generally,
any noun referring to an animal or an inanimate item as
a complete whole takes /pum/. |
| /nàríel/ |
‘coconut’ |
| /nàríel
púm hní/ |
‘thepair
of coconut’ |
/ á/ á/ |
‘fish’ |
/ à
púm/ à
púm/ |
‘the
particular whole fish’ |
| /ín/ |
‘house’ |
| /ín
pùm/ |
‘the
whole house’ |
/kú: / / |
|
|
|
|
| Any
noun referring to trees, plants etc. take this definitive. |
/thí / / |
‘tree’ |
/thí kù:
kù: / / |
‘the
particular tree’ |
/tlà / / |
|
|
|
|
| Generally,
this is used to refer to a particular portion of some
animal or thing. |
/ á/ á/ |
‘fish’ |
/nà
tlà / / |
‘a
piece of a fish’ |
| /píl/ |
‘soil’ |
/píl
tlá / / |
‘a
clod of soil’ |
|
|
|
|
Hmar
does not have grammatical gender. What it has is only
natural gender or sex-reference which is restricted
to the higher class of animate nouns. The gender distinction
of the noun-whether it is in the subject slot or in
the predicate slot-has no bearing on the adjectives,
verbs or any other elements in the sentence. Hmar makes
the gender distinction of nouns only when it is necessary
to do so for semantic realisation.
The marking of gender of the nouns has no grammatical
necessity.
Since the gender distinction in Hmar is based on natural
gender or sex reference it is all but natural to identify
only two genders-masculine and feminine. There is nothing
like neuter gender. There are, however, few cases traditionally
considered as common gender, which again have no grammatical
relevance. In order to make the masculine-feminine distinction
of nouns Hmar uses one of the two devices : |
| i. |
Use
of pairs of opposite lexical entries, or
Use of attributives referring to male or female
after the noun. |
| ii. |
Of
these, the latter device is more productive. |
|
| 3.2.1.6.1 |
Use
of Pairs of Opposite Lexical Entries |
|
Hmar
makes gender distinction of few words by using pairs
of opposite lexical entries. They fall in in line with
‘Items and Arrangement’ analysis of Hocket2. Such pairs
of words have no formal relationship. Given below are
few examples : |
/àrkh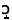 : : / / |
‘cock’ |
/árpúi/ |
‘hen’ |
| /pá/ |
‘father’ |
/nú/ |
‘mother’ |
| /pàsál/ |
‘husband/man' |
/nùhmèi/ |
‘wife/woman’ |
| /pàsálè/ |
‘boy/small
man' |
/nùhmèité/ |
‘girl/small
woman’ |
| /bíelpa/ |
|
/íelnù/ |
|
/l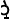 mpá/ mpá/ |
‘lover’ |
/l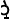 mná/ mná/ |
‘beloved’ |
| /sàkéi
cál/ |
‘tiger’ |
/kéipúi/ |
‘tigress’ |
|
|
|
|
|
| 3.2.1.6.2 |
Use
of Attributives |
|
The
other device of distinguishing gender in Hmar is the
use of attributives referring to male or female after
the nouns. All such attributives occurs as the second
constituents. |