|
(3)
|
In the clusters of three consonants C1C2C3
in the intervocalic position, the syllabbic cut is in two ways:
|
|
(i)
|
C1C2 forms the coda of
the preceding syllable when either they are homorganic consonants or C1
is /r/ and C3 forms the onset of the following
syllable. (ii) In all the other cases the syllabic cut is after C1
which forms the coda of the preceding syllable and C2C3
as the onset of the following syllable. Examples are:
|
|
Type-i
|
|
/bamb. i/ i/
|
‘elephant’s trunk’
|
|
/s nt.ro/ nt.ro/
|
‘orange’
|
|
/pInj.ro/
|
‘cage’
|
|
/m st.yo/ st.yo/
|
‘arrogant’
|
|
/khUrk.¸o/
|
‘to itch’
|
|
/šagIrd. i/ i/
|
‘female pupil’
|
|
|
Type-ii
|
|
/kut.ryo/
|
‘dog’
|
|
/c d.rya d.rya i/ i/
|
‘land lady’
|
|
/ak. yo/ yo/
|
‘arrogant’
|
|
/ w.sr€ w.sr€ i/ i/
|
‘female officer’
|
|
Types of Syllable
|
|
From the syllabic structure (C1C2)V(C1C2)
all types of syllables except C1C2VC1C2
are possible. No single syllable is found to have two consonants as the
onset and coda. Following are the types of syllables found in the
language:
|
|
1.
|
V
|
/ .car/ .car/
|
‘pickle’
|
|
|
/a. o/ o/
|
‘niche, hole in the wall’
|
|
|
/€.  k/ k/
|
‘spectacles’
|
|
2.
|
VC
|
/It/
|
‘here’
|
|
|
/al. o/ o/
|
‘nest’
|
|
3.
|
CV
|
/ma/
|
‘in’
|
|
|
/bu.ţo/
|
‘plant, tree’
|
|
|
/as.ro/
|
‘support’
|
|
4.
|
CVC
|
/ ab/ ab/
|
‘pond’
|
|
|
/l k/ k/
|
‘waist’
|
|
|
/m .dan/ .dan/
|
‘ground’
|
|
5.
|
VC1C2
|
/ang. i/ i/
|
‘finger’
|
|
|
/ nj/ nj/
|
‘finger joint’
|
|
6.
|
CVC1C2
|
/b rf/ rf/
|
‘ice, snow’
|
|
|
/dost/
|
‘friend’
|
|
|
/band.ri/
|
‘she monkey’ |
|
|
/k tUng. tUng. o/ o/
|
‘puppy’
|
|
7.
|
C1C2V
|
/tr€/
|
‘three’
|
|
|
/dro.go/
|
‘watchman’
|
|
|
/pya. o/ o/
|
‘cup’
|
|
|
/n w. w. yo/ yo/
|
‘caught’
|
|
|
/  k. k.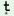 r€. r€. i/ i/
|
‘lady doctor’
|
|
8.
|
C1C2VC
|
/prit/ |
‘love’ |
|
|
/jye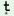 h/ h/
|
‘husband’s elder brother’
|
|