| we |
buţa
|
k ppẽ ppẽ |
tha
|
|
‘They
|
were
|
cutting
|
the
|
trees’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
|
2 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
geri
|
jy€
|
thi
(IIIp.sg.fem.)
|
|
‘The
|
girl
|
was
|
going’
|
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
h m m
|
jã
|
thĩ(Ip.pl.fem.)
|
|
‘We
|
were
|
going’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
(c.3.) Present Perfect
|
|
hũ
|
k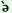 r r
|
geyo
|
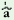
|
|
‘I
|
have
|
gone
|
home’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
hem
|
n 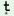 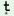 hã hã
|
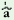
|
(mas.pl.Ip.)
|
|
‘We
|
have
|
run’
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
t m m
|
k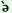 r r
|
geya
|
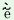
|
|
‘You (pl.)
|
have
|
gone
|
home
|
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
wo
|
k r r
|
geyo
|

|
|
‘He
|
has
|
gone
|
home’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
gerĩ
|
g ĩ ĩ
|
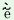
|
(fem.pl.IIIp.)
|
|
‘The
|
girls
|
have
|
gone’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
we
|
It
|
aya
|
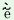
|
(mas.pl.IIIp)
|
|
‘They
|
have
|
come
|
here’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
(c.4.) Past Perfect
|
|
gero
|
k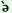 r r
|
geyo
|
tho
|
|
‘The
|
boy
|
had
|
gone
|
home’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
1 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
m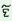
|
y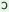
|
k m m
|
kIyo
|
tho
|
|
‘I
|
had
|
done
|
his
|
work’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1 |
5 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
|
| |
|
|
|
Us
|
nE€
|
jyad€
|
k m m
|
kIya
|
|
‘He
|
had
|
done
|
many
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
1-2 |
6 |
5 |
3 |
|
tha
(mas.pl.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
works’
|
|
|
|
|
6
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
(c.5) Present obligative : Infinitive form taking the present tense
auxiliary.
|
|
m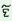
|
k m m
|
k r r o o
|

|
|
‘I
|
have
|
to
|
work’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
|
2-3 |
|
|
|
|
Us
|
n€
|
ja o o
|

|
|
‘He
|
has
|
to
|
go’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1-2 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
|
(c.6) Past obligative : Infinitive form when takes the past tense
auxiliary.
|
|
gera
|
n€
|
ja o o
|
tho
|
|
‘The
|
boy
|
had
|
to
|
go’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
1-2 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
| |
|
m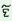
|
kItab
|
p  ni ni
|
thi
|
|
‘I
|
had
|
to
|
read
|
the
|
book’
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
1 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
2 |
|
|
(c.7) Desiderative : Contingent forms can also take the desiderative
auxiliary.
|
|
tũ
|
jyE
|
a
|
d€
|
k m m
|
ho
|
jy€
|
a
|
|
‘If
|
you
|
had
|
gone
|
the
|
work
|
|
1
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
1 |
|
2-3 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
would
|
have |
been |
done’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6-7-8
|
|
|
|