| 1. |
jom ‘to eat’ |
jo-jom |
‘eating’ |
|
sen ‘to walk’ |
se - sen |
‘walking’ |
|
| 2. |
ir ‘to reap’ |
ir-ni? } |
‘reaper' |
|
| 3. |
jÚom‘to
eat’ |
jom-tan-i? |
‘one who is eating’ |
|
| 4. |
maraŋ |
big |
maraŋ
- i |
i bigness. |
|
hu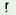 iŋ
iŋ |
‘small’ |
maraŋ
- i |
i ‘smallness’ |
|
| 2.2.
|
Number.
|
| According to Cook (1965:119 . 120), the
inanimate stems need not take the number sufixes. The stem
can express all the three numbers in inanimate nouns. In
Bhumij number marking is obligatory including the inanimate
nouns. |
| 2.3.
|
Numerals.
|
| Mundari has retained the original numeral
system of Munda whereas Bhumij has retained the original
numeral system of Munda only upto six and all the numerals
above six are borrowed from Oriya. |
|
3. |
VERB |
|
3.1.
|
Causative verb: |
| The causative verbs, in Mundari,
are derived in four different ways: 1. prefixing a-,
suffixing - iri, -ic&i,
and riko. In Bhumij, the causative verbs are derived by two
different ways: 1. Prefixing -a, 2. suffixing -ic&i.
Bhumij does not have the suffixes iri and riko to derive the
causative verbs. |
| 3.2. |
Tense markers: |
| 3.2.1.
|
Past tense: |
Mundari has eight past tense markers.
In Mundari, aspect markers function as tense markers also. |
Mundari (Sinha : 1975)
|
| ked |
simple past (tr.) |
| ken |
" "(intr.) |
|
| len |
anterior past (intr.) |
| led |
,,
,, (tr.) |
| ken |
ncomplete past (tr.) |
| jan |
indefinite past (intr.) |
| akad` |
perfect tense (tr.) |
| akan |
,, ,,
(intr.) |
|
Bhumij
|
| l } |
} transitive past |
| k } |
|
| jan |
intransitive past. |
| ked |
transked itive past alternates with l. |
|
|
ken and len are past tense markers in Mundari whereas in Bhumij, they are aspect markers. The anterior past led in Mundari is not
found in Bhumij. The transitive past tense markers l, and k which are found
in Bhumij are not available in Mundari.
|
|
3.2.2.
|
Present tense:
|
|
Mundari has five present tense markers whereas Bhumij has
no present tense marker.
|
Bhumij (Sinha : 1975)
|
| O
|
ndeterminate present. |
| tan |
definite present |
| jad |
ndefinite present |
| akad+ge |
continuative present (tr.) |
| akan+ge |
,,
,, (intr.)
|
|