| |
|
|
| 6.3.0
Causativization13 |
| |
| 6.3.1
Causatives are found in three distinct classes in Angami : |
| |
| (1)
Causatives which do not morphologically differ from the
non-causatives or intransitives but which have obligatory manner
or instrument markers prefixed to them. When the manner makers
are prefixed, the initial consonant of the verb is aspirated.
Typically, verbs becoming causatives in this manner are
‘included-object’ ‘included-instrument’ verbs. |
| |
1. t ®
® |
bi th th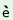
|
‘to cut rope (with hand)’ |
| ‘to give way’ |
ci th th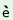 |
‘to break by pulling at a hung object’ |
| (as of rope) |
|
|
| |
d th th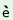 }
} |
‘to cut with dao’ |
| |
r th th |
|
| |
r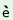 th th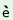
|
‘to cut with saw’ |
| |
b th th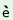
|
‘to cut with scissors’ |
| |
d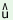 th th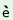
|
‘to cut with blunt implements like axe’ |
2. pru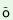 ®
® |
v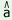 phru phru
|
‘to break glass (by dropping)’ |
| ‘to break’ |
bi phru phru
|
‘to break glass (with hand)’ |
| (glass, pot) |
|
|
| |
d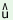 phru phru
|
‘to break glass (with any implement)’ |
| |
p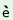 phru phru
|
‘to break glass (with something that is
thrown)’ |
3. pru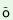 ®
® |
s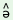 phru phru
|
‘to split or break party etc. |
| ‘to split’ |
|
intentionally’ |
| (class, party) |
bi phru phru
|
‘to split or break party etc. because of
circumstances, like |
| |
|
inability of the leadership’ |
|
| |
| ___________ |
|
13The term ‘causativization’ I have used,
interchangeably, with ‘transitivization’, since the verbs
discussed here typically have an underlying ‘cause + happen’
configuation. |
| |
4. c ®
® |
bi ch ch
|
‘to break windowpane by hand’ |
| ‘to break |
|
|
| (windowpane |
p ch ch
|
‘to break windowpane by |
| bamboo)’ |
|
throwing something’ |
| |
d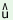 ch ch
|
‘.............with any implement’ |
| |
k s s ch ch
|
‘............due to external impact’ |
5. ts ®
® |
ci tsh tsh
|
‘to break tree with hands’ |
| ‘to break or |
d tsh tsh
|
‘.........with dao or other big implements’ |
| cut tree’ |
d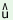 tsh tsh
|
‘...........with heavy implements like axe’ |
| |
w tsh tsh
|
‘to fell tree with any implement’ |
|
| |
(2)
Causatives which are morphologically different from the
non-causatives. This has three sub-classes : (i) causatives
which are derived from non-causatives by prefixing p (ii) morphologically marked non-causatives made causative by the
replacement of the non-sausative marker r
(ii) morphologically marked non-causatives made causative by the
replacement of the non-sausative marker r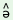 by the causative marker k
by the causative marker k (iii) Non-causatives become causative when the intrasitive
marker r
(iii) Non-causatives become causative when the intrasitive
marker r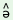 is deleted is deleted |
| |
(i) lh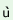 |
® |
p lh lh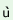
|
‘to grow (animate beings)’ |
l |
® |
p l l
|
‘to make any liquid hot or to boil’ |
t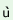 |
® |
p t t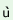 |
‘to kindle fire’ |
mh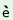 |
® |
p mh mh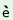
|
‘to extinguish fire’ |
z |
® |
p z z
|
‘to melt’ |
|