| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| 4.8.
Quantifiers: |
|
The Quantifiers in Angami are : |
(1) hu ‘some’
(2) hu
‘some’
(2) hu y y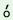 ‘a little ; a few’
‘a little ; a few’ |
(3) k kr kr ‘many’
(4) p
‘many’
(4) p t t ‘all’
‘all’ |
| |
hu y y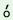 with the diminutive suffix -y
with the diminutive suffix -y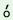 denotes a smaller quantity than hu
denotes a smaller quantity than hu |
dz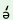 hu hu ‘some water’ ‘some water’ |
dz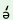 hu hu y y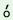 ‘a little water’
‘a little water’ |
l s s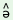 d d hu
hu ‘some books’ ‘some books’ |
l s s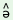 d d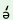 hu
hu y y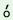 ‘a few books’ ‘a few books’ |
ih mi mi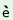 hu
hu ‘some people ‘some people |
th mi mi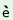 k
k kr kr ‘many people ‘many people |
 m k m k kr kr ‘many mangoes’ ‘many mangoes’ |
l s s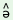 d d k
k kr kr ‘many books’ ‘many books’ |
 k k p
p t t (k
(k )
‘we all’ )
‘we all’ |
th v v p
p t t (k (k )
‘all pigs’ )
‘all pigs’ |
l s s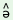 d d p
p t t (k (k )
‘all books’ )
‘all books’ |
|
The Quantifiers hu ,
hu ,
hu y y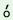 and k
and k kr kr do not take -k
do not take -k , the
plural marker as a rule. It is optional with p , the
plural marker as a rule. It is optional with p t t ‘all’.
‘all’. |
| |
| 5.0.0.
The Adjective |
|
Angami like Japanese has no morphological form-class of
adjectives. Under the larger class ‘Noun Attribute’ are subsumed
quantifiers, numerals, demonstratives and verbs or verbal
participles which function as noun attributes of quality. These
verbs or verbal participles functioning as Noun attributes of
quality will be called ‘adjectives’ in this grammar. |
| |
(1) Verbs functioning as adjectives |
k s s
|
‘new’ |
t
|
‘black’ |
k t t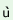 |
‘equal’ |
kr
|
‘white’ |
k th th kr kr
|
‘funny’ |
d
|
‘plump’ |
|
| |
|
(2) Verbal particliples functioning as adjectives. This is a
much larger class. A typical Angami adjective is formally a
verbal (relative) participle. |
 i i
|
‘to die’ |
k  i i
|
‘dead’ |
z v v
|
‘to be beautiful’ |
k z z v v
|
‘beautiful’ |
z  u u
|
‘to be ugly’ |
k zi zi u u
|
`ugly' |
v ’
’ |
‘to be good’ |
k v v |
‘good |
|
 u u
|
‘to be bad’ |
k  u u
|
‘bad’ |
r kri kri
|
‘to be tall’ |
k r r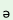 kri kri
|
‘tall’ |
r
|
‘to be costly’ |
k r r
|
‘costly’ |
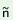 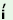
|
‘to be rich’ |
k 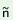 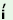
|
‘rich’ |
|
| |
|
(3) Substantives functioning as adjectives. They precede the
head noun, unlike the other adjectives. |
k ci ci s
s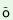 z z
|
‘stone wall’ |
k khri khri c
c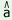 l l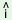
|
‘love poem’ |
s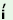 m
m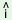 z z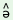
|
‘wood(en) table’ |
khr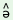 w w k
k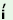 |
‘glass house’ |
k rie rie ki
ki |
‘bamboo house’ |
|
| |
|
5.0.1 It should, however, be noted that there is no
formal criterion to distinguish between N+N phrases from N+N
compoud words. |
|
|
5.0.2 Some descriptive adjectives belong to both the
categories. |
t
|
or |
k t t
|
‘black’ |
kr
|
or |
k kr kr
|
‘white’ |
d
|
or |
k k k
|
‘plump’ |
z |
or |
k z z |
big’ |
|
| |
5.1.0
Concord : Concord between the adjective (the verbal participle)
and the substantive is optional. Generally, the adjective is not
declined to agree with the substantive. But for emphasis or to
clearly distinguish the gender of the substantive, the gender
marker pf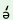 and the
diminutive marker y and the
diminutive marker y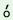 are added to the adjective in agreement with the substantive.
are added to the adjective in agreement with the substantive. |
| |
th pf pf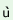 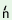 y y 1
k 1
k v v 2
pu 2
pu 3
> th 3
> th pf pf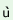 ny ny 1
k 1
k v v y y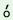 2
pu 2
pu 3
‘a3good2boy1’ 3
‘a3good2boy1’ |
th n n ny ny 1
k 1
k z z v v 2
pu 2
pu 3
> th 3
> th n n ny ny 1
k 1
k z z v v pf pf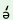 2
pu 2
pu 3
‘a3beautiful girl1’ 3
‘a3beautiful girl1’ |
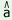 1
ny 1
ny pf pf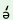 3
k 3
k m m yi yi 3
> 3
> 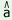 1
ny 1
ny pf pf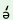 2
k 2
k m m yi yi pf pf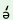 3
‘my1 famous3
daughter2’ 3
‘my1 famous3
daughter2’ |
|
| Otherwise,
adective uaually follows the substantive that is qualifies. |
|
th mi mi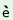 1,
k 1,
k lu lu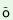 2
‘fate2man1’ 2
‘fate2man1’ |
th n n ny ny 1
k 1
k m m h h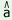 2
‘shy girl’ 2
‘shy girl’ |
t f f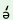 1
k 1
k t t 2
‘black2dog1’ 2
‘black2dog1’ |
k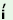 1
k 1
k z z 2
k 2
k z z v v 3
‘big2beautiful3
house1’ 3
‘big2beautiful3
house1’ |
| |
The
Number marker and the article follow the adjective. |
|
l s s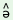 d d 1
k 1
k v v 2-k 2-k 3
‘the3good2books1’ 3
‘the3good2books1’ |
t ku ku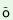 1
k 1
k t t 2-ni 2-ni 3‘the two3black2
sheep1’
3‘the two3black2
sheep1’ |
ny 1
k 1
k z z v v 2
pu 2
pu 3
‘one3handsome2boy1’ 3
‘one3handsome2boy1’ |
t f f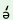 1
k 1
k kr kr 2- 2-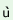 3
‘the3white2dog1’ 3
‘the3white2dog1’ |
| |
| Numerals,
demonstratives and quantifiers follow the adjective in that
order. |
| |
l s s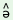 d d 1
k 1
k v v 2
p 2
p h h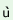 3
‘five3good2books1’ 3
‘five3good2books1’ |
m z z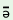 1
k 1
k z z 2
s 2
s 3
‘three3big2tables1’ 3
‘three3big2tables1’ |
l s s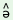 dA1
k dA1
k v v 2
m 2
m pf pf 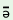 3
s 3
s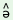 k k 4
p 4
p t t (k (k )5
‘All5 those4 twenty3
good2books1’ )5
‘All5 those4 twenty3
good2books1’ |
|
|
| The
structure of Noun+Modifier constructions may be formalized as |
| |
| N
±adj.±numera±dem.
±quantifier ±
number marker |