| |
|
|
(27)(a)Pu
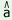 k k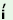 v
v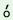 r r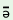
|
‘he came to me’ |
(b) pu pu
pu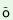 k k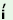
|
‘to his father’ |
(c)
k p p th th 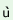 k
k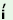 |
‘To the teacher’ |
(d)  k k p p ny ny pf pf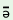 k
k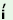 |
‘To God’ |
| |
|
(28)(a)
ga h h t t n
n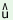 |
‘To Gauhati’ |
(b)
l s s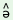 k k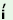 n
n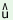 |
‘To (the) school’ |
(c) 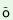 f f s
n s
n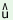 |
‘To (the) office’ |
| |
|
(29)(a)
k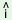 j j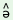 th th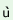 g
g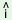 |
‘To (the) hill’ |
(b) j pf pf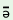 g
g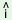 |
‘To Japh (a hill)’
(a hill)’ |
(c) t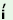 g
g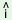 |
‘To (the) sky; to heaven’ |
(d) khr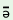 g
g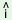 |
‘To (the) moon’ |
(e) th m m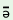 g
g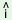 |
‘To (the stars’ |
(g) sa ns
k ns
k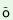 l l j
g j
g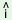 |
‘To (the) Science college’ |
| |
(which is at a higher altitude at Kohima) |
(30)(a) w 1 1  k k p p ny ny pf pf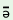 2
k 2
k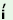 3 3
|
‘We1 should5
pray4 to3 God2’ |
ch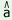 4
m 4
m r r  u u 5 5 |
|
(b)  1
pu 1
pu k
k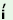 2
ch 2
ch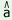 3
k 3
k ts ts 4 4
|
‘I1 asked4
him2 (the) way3’ |
(c) pu 1 1
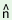 k
k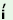 2
p 2
p s s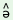 ty
ty 3 3
|
‘He1 will tell3
you2’ |
|
| |
3.6.1.
Animate (non-human) nouns do not take the Goal case. marker.
Instead they take the locative adverb p ny ny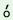 ‘near’
‘near’ |
| |
(31) nh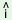 c c ny ny k k 1 1 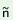 i i ny ny 2
p 2
p ny ny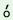 3
v 3
v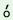 4
‘The children1 went4
near3 the cat2’ 4
‘The children1 went4
near3 the cat2’ |
| |
| 3.6.2. The
Directional allo-case denotes the direction, typically, of
motion verbs. It is marked by tsa ‘towards’ when the direction
is on a plane. |
| |
(32) (a) b li li 1 1
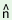 2
k 2
k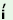 3
ts 3
ts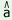 4
v 4
v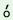 5 5
|
‘Balie1 went5
towards4 your2
house3’ |
(b)
k r r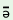 ts
ts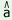 |
‘towards the river’ |
|
| |
When g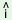 follows substantives (which do not form part of the finite set
suggested in 3.6.0), it denotes direction upwards rather than
the fact that (the referent of) the substantive itself is on a
higher altitude
follows substantives (which do not form part of the finite set
suggested in 3.6.0), it denotes direction upwards rather than
the fact that (the referent of) the substantive itself is on a
higher altitude |
| |
| Thus, |
(33)(a)  k k 1
k 1
k t t bm bm n n r2 r2
|
‘They1 went4
up3 (the skyscraper |
g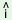 3
v 3
v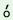 4 4
|
that is) Kutub Minar2’ |
(b)  1
k 1
k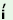 2
g 2
g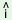 3 3
 i i 4 4
|
‘I1 went4
up3 (the) house2
(perhaps to the roof. . .)’ |
|
| |
3.6.3 The
Extent allo-case denotes the extent either in space or time. It
is marked by the postpostion k ts ts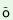 ‘upto’
‘upto’ |
| |
 1
b 1
b s
st s
st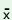 nd2
k nd2
k ts ts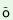 4
v 4
v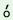 4 4
|
‘I1 went2
upto3 (the) bus stand2’ |
 k k 1
l 1
l s s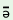 k k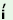 2
k 2
k ts ts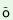 3
v 3
v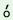 4 4
|
‘They1 went4
upto3 (the) school2’ |
thi k
k ts ts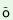
|
‘upto today’ |
b k
k r r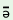 k
k ts ts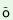
|
‘upto 10 ‘O’ clock’. |
|
| |
| On the
temporal plane, there is no formal difference between Goal -
Extent. |
| |
3.6.4 The
Goal case is unmarked when it denotes the goal of
three-participant verbs like pi ts ts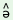 ‘give’ or k
‘give’ or k ts ts send’. i.e. the indirect object of such verbs (the traditional
Dative) is not marked.
send’. i.e. the indirect object of such verbs (the traditional
Dative) is not marked. |
| |
(34)(a) r k k 1
k 1
k ni ni 2
pi 2
pi 3 3
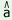 4
ts 4
ts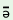 ci ci 3 3
|
‘Give3 me4
two2 rupees1’ |
(b)
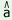 pu
pu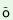 1
r 1
r k k 2
kri 2
kri pu
pu 3
k 3
k ts ts pi
pi 4 4
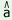 5
ts 5
ts 4 4 |
‘My father1 sent4
me5 hundred3
rupees2’ |
|
| |
3.7 The
Benefactive case denotes that the action or state indentified by
the verb is done for or in the interest of another being-
animate or inanimate. This may also be called ‘purposive’ case.
It is marked by l . . |
| |
(35)(a)
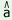 l
l |
‘for me; for my sake’ |
(b)
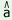 pu
pu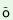 l l
|
‘for my father’s sake’ |
(c)
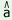 v
v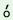 k k l
l |
‘for my pigs’ |
(d) miz l
|
‘for the table’ |
|
| |
3.8.0 The
Instrumental case expresses the means (inanimate force or
object) by which the action identified by the verb is done. It
is marked for abstract substantives by s (d (d )
and for concrete substantives either by pi )
and for concrete substantives either by pi or by s
or by s (d (d )
with pi )
with pi being much
more frequent. being much
more frequent. |
| |
(36)(a)
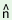 ket
ket rh rh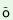 s
s (d (d ) )
|
‘with your advice’ |
(b)
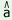 k
k khru khru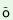 h
s h
s |
‘with my help’ |
| |
|
(37)(a)  mh mh pi
pi |
‘with our eyes’ |
(b) ph ph z z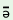 pi
pi |
‘with out feet’ |
(c) r k k k
k ni ni pi
pi |
‘for/with two rupees’ |
(d) b r r 1
h 1
h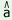 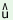 2
s 2
s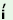 3
pi 3
pi 4
tsh 4
tsh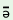 5 5
|
‘This2 chair1
is made5 of wood3’ |
|
| |
| 3.8.1 The
Instruments of motion are expressed by Locative or Sociative or
Comitative case markers. |
| |
(38) (a)  1
b 1
b s2
n s2
n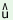 n n /g /g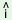 n n 3
v 3
v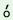 r r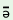 4 4 |
‘I1 came4
by3 bus2’ |
(b)  k k 1
tr 1
tr n2
n n2
n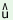 n n 3
v 3
v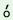 4 4
|
‘They1 went4
by3 train2’ |
(c)  1
g 1
g r r 2
z 2
z 3
ty 3
ty t t ty
ty 4 4
|
‘I1 will go4
by3 bus2’ |
(d)  1
ba 1
ba s s kl2
s kl2
s 3
l 3
l s s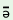 k k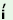 4 4
|
‘I1 go6
to6 school4 by3
cycle2’ |
n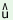 5
y 5
y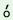 y y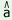 6’ 6’ |
|
|