|
It is also interesting to note that the durative aspect is also indicated by the auxiliary verb man ‘to be’. When the present tense form of auxiliary is added to the present adverbial participle it indicates present durative sense.
|
| nana: tinjok ma:hinan |
‘I am eating’ |
mi: tinjok ma:hini:r tinjok ma:hini:r |
‘you are eating’ |
| ad tinjok ma:hinta: |
‘it/she is eating’ |
|
|
When the past form of the auxiliary man ‘to be’ is added to the past adverbial participle it means past or non-past durative aspect or past perfective.
|
| nannna: inji: mata:n |
‘I had told/
I was telling/
I shall be telling’ |
ma: hanji: mato:m hanji: mato:m |
‘we had gone/
we were going/
we shall be going’ |
wo:r hu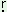 si: mato:r si: mato:r |
‘they had seen/
they were seeing/
they shall be seeing’ |
|
|
The process of verb stem inflection discussed in the foregoing pages is presnted below in the form of a diagram.
|
| Verbal Inflection |
|
 Presnt suffix Presnt suffix |
 PE1 PE1  |
1. Presnt tense |
|
 Past Suffix Past Suffix |
 PE2 PE2  |
2.Past tense |
|
 Future suffix Future suffix |
 PE3 PE3 |
3.Future tense |
|
 Habitual Suffix Habitual Suffix |
 PE4 PE4  |
4. Habitual tense |
|
 Negative Negative |
 PE5 PE5  |
5. Negative |
|
 Prhibitive---suffix Prhibitive---suffix |
 Pl. Pl. |
6. Prohibitive |
|
 Imperative-- suffix Imperative-- suffix |
 Pl. Pl. |
7. Prohibitive |
|
 Past suffix Past suffix |
 Conditional suffix Conditional suffix |
8. Present conditional |
|
 Past perfective Past perfective |
 Conditionalsuffix Conditionalsuffix |
9. Pastconditional |
|
 Negative suffix Negative suffix |
 Conditional suffix Conditional suffix |
10. Contrafactual conditional |
|
 Durative Durative |
 PE6 PE6 |
11. Present durative |
|
 Past suffix Past suffix |
 Durative suffix Durative suffix  PE6 PE6 |
12. Past durative |
|
 Future suffix Future suffix |
Durative suffix  PE6 PE6 |
13. Future durative |
|
 Past adverbial suffix Past adverbial suffix |
 Aux Aux Durative- Durative-  PE7 PE7 |
14. Past perfective |
|
 Present Aux adverbial suffix Present Aux adverbial suffix |
 Durative Durative  PE7 PE7 |
15. Imperfective |
|
 Infinitive suffix Infinitive suffix |
|
 16. Present infinitive 16. Present infinitive |
|
 Infinitive suffix Infinitive suffix |
 aux aux  |
17. Infinitive as optative |
|
 Verbal suffix Verbal suffix |
 Aux Aux PE PE  |
18. Obligative |
|
|
|
|