| 7.8.8. Conditional |
|
Condtional verbs are of three kinds:
|
| (1) Present conditonal, |
| (2) Past conditonal, and |
| (3) Contra-factual conditional. |
|
| 7.8.8.1. Present Conditional |
|
Present conditional is formed by the addition of conditional suffix -e:k to the past verb stem.
|
| Examples: |
|
tin- |
‘to eat’ |
tit-t-e:k |
|
a - - |
‘to cook’ |
a - - -e:k -e:k |
|
wi s- s- |
‘to leave’ |
wi·s-t-e:k |
|
gu: - - |
‘to sleep’ |
gu: -t-e:k -t-e:k |
|
wa:y |
‘to come’ |
wa:t-t-t:k |
|
ke:nj- |
‘to listen’ |
ke:nj-t-e:k |
|
a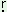 - - |
‘to weep’ |
ar8-t-e:k |
|
we:h- |
‘to tell’ |
we:h-t-e:k |
|
wa:r- |
‘to sing’ |
wa:r-t-e:k |
|
pu - - |
‘to born’ |
pu -t-e:k -t-e:k |
|
hi:- |
‘to give’ |
hi:-t-e:k |
|
| 7.8.8.2. Past Conditional |
|
When the conditional suffix -e:k is added the past perfect form of a verb it indicates past conditional.
|
| Examples: |
|
tin- |
‘to eat’ |
tinjimak-e:k |
|
wi s- s- |
‘to leave’ |
wi simat-e:k simat-e:k |
|
gu: - - |
‘to sleep’ |
gu: simat-e:k simat-e:k |
|
ke:nj- |
‘to listen’ |
ke:njimat-e:k |
|
a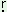 - - |
‘to weep’ |
a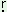 simat-e:k simat-e:k |
|
hi:- |
‘to give’ |
hi:simat-e:k |
|