CHAPTER
I |
|
ETHNOGRAPHY |
|
| 1.1 Introduction |
|
Brief ethnographic descriptions of Yeravas are found
in several published works such as Memoir of the
Codugu Survey Vol. II by Connor (1870), Ethnographical
Compendium on the Castes and Tribes found in the Province
of Coorg by Richter (1887),"Coorgs and Yeruvas"
by Holland (1901). The Coorg Tribes and Castes
by L.A. Krishna Iyer (1948) and Archaeology o.f Coorg
by K.K. Subbayya (1978). Here brief ethnographic description
of Yeravas based mainly on the data collected and analyzed
by this investigator is presented. |
|
| 1.1.1 Kodagu |
| The Yeravas are an important
tribe of Kodagu district popularly known as Coorg district.
The Kodagu district is the smallest district in Karnataka
and is situated in the Southern part of Karnataka. It
is small both in area and in population. |
| This Kodugu district of 4104
square kilometres area is situated between 11°56'
and 12°50' North Latitude and 75°22' and 76°12'
East Longitude. The maximum length of the district from
North to South is 96 kilometres and maximum breadth from
East to West is 64 kilometres. Within this area Yerava
population is concentrated in the region between 11°56'
and 12°15' North Latitude, and 75°45' and 76°12'
East Longitude. |
| The four Nads that
come within this area are (see Map 1) Srimangala Nad,
Ponnampet Nad, Ammatti Nad and Virarajapet Nad. Out of
these four Nads, the Yerava population is concentrated
mostly in Srimangala Nad, Ammatti Nad and Ponnampet Nad.
This district is bound in North by Hassan district, in
East by Mysore district, in West by South Canara district
of Kamataka. And in South it is bound by Cannanore district
of Kerala State. In South, Bramhagiri hills serves as
a natural boundary between Kodagu district and Kerala
State. |
|
| 1.1.2 Mountains |
The Kodagu district is known
as the district of mountains and forests. The Bramhagiri
hills of South, the Bramhagiri hills of North and Pushpagiri
hills of North West are some of tlle important hills to
mention. The highest mountain is Tadiyandamole with the
height of 5729' from the mean sea level. There are two
types of forests in Kodugu. The male ka: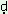 u and ka u and ka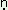 ive
ka: ive
ka: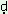 u, namely, the forests of mountains and the forests
of valleys and lower hills. The Madikeri (Mercara) town,
the head quarters of the district, is 3809' above the
sea level. The four Nads mentioned earlier are on the
plateau of South Bramhagiri hills. Srimangala, Ponnampet,
Virarajapet and Ammatti are at a height of 2782', 2811',
2981', and 3061' from the sea level. u, namely, the forests of mountains and the forests
of valleys and lower hills. The Madikeri (Mercara) town,
the head quarters of the district, is 3809' above the
sea level. The four Nads mentioned earlier are on the
plateau of South Bramhagiri hills. Srimangala, Ponnampet,
Virarajapet and Ammatti are at a height of 2782', 2811',
2981', and 3061' from the sea level. |
| The Kodagu district experiences
three seasonal winds. The West wind, the North-East wind,
the South-West wind, during monsoon, after monsoon and
during the rest of the year respectively. |
The average
maximum temperature of the district is 28.6°C or
83.5°F and the average minimum temperature is 17.8°C
or 64.0°F. The Kodagu district has an average rainfall
of 2725.5 mm annually and the Virarajapet taluk has
an average rainfall of 2671.8 mm annually. |
|
|
|