4.21.1.4.2. 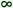 -Ø -Ø |
ka  -Ø (5.19) -Ø (5.19) |
> |
ka  u u |
‘bundle’ |
| kutt-Ø (5.19) |
> |
kuttu |
‘stab’ |
a i-Ø i-Ø |
> |
a i i |
‘beat’ |
kė: -Ø(5.19) -Ø(5.19) |
> |
kė: u u |
‘spoil’ |
ju: -Ø (5.19) -Ø (5.19) |
> |
ju: u u |
‘heat’ |
4.21.1.4.3 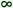 -vu -vu |
| sa:-vu |
> |
sa:vu |
‘death’ |
| 4.21.1.5 Instrument of an action |
| St. {-i} |
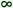 -i, -i, 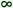 -ige, -ige, 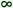 -ge -ge |
4.21.1.5.1. 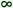 -i -i |
| udav-i |
> |
udavi |
‘help’ |
mu: -i -i |
> |
mu: i i |
‘lid’ |
4.21.1.5.2. 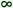 -ige -ige |
| a:s-ige |
> |
a:sige |
‘bed’ |
e  -ige -ige |
> |
e  ige ige |
‘counting’ |
4.21.1.5.3 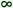 -ge -ge |
a u-ge u-ge |
> |
a uge uge |
‘cooking’ |
| 4.22 Modifiers |
| All the adjectives are treated under the nominal modifiers and the adverbs under the verbal modifiers. The modifiers are indeclinable. The modifiers are classified on the basis of their semantic qualities and syntactic function. Modifiers are broadly classified into three classes. They are, |
| (i) Simple |
| (ii) Derived, and |
| (iii) Reduplicated |
| 4.22.1 Nominal Modifiers |
| 4.22.1.1. Simple Adjectives |
| Simple adjectives are monomorphemic in nature. Simple adjectives include the numerals and the other types of qualitative and quantitative adjectives. The qualitative adjectives can be subgrouped into different types which denote colour, taste, etc. Quantity is being denoted by the quantitative adjectives. |
 |
 |
|