|
edė
|
sėk m m
|
gure-n?
|
‘Whose horse is
that?’
|
|
that
|
whom
|
horse int
|
|
|
|
| 4.14.3.
Tag-Question : |
In tag questions /-la /
is the interrogative marker. However, the marker /-ne/, which is borrowed
from Assamese, is also used, but its use is restricted to the second
person future tense. /
is the interrogative marker. However, the marker /-ne/, which is borrowed
from Assamese, is also used, but its use is restricted to the second
person future tense. |
|
bļ
|
ayine
|
ayi-l
|
‘He is good, isn’t
he?’
|
|
he
|
good
|
good int
|
(He (is) good, is
(he) good?)
|
|
bļ
|
edėm
|
ķka-ķla ? ?
|
‘He did it, didn’t
he?’
|
|
he
|
this
|
do t
|
(He did it, did
(he) do?)
|
|
bulu
|
mėlo
|
|
‘They went yesterday,
didn’t they?’
|
|
they
|
yesterday go t
|
go t go int
|
|
|
n¨
|
g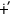 -la -la
|
g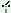 -ye-ne? -ye-ne?
|
‘You will go, won’t
you?’
|
|
you
|
go tense
|
go t int
|
|
|
|
| Second
person future marker /laN/ and
the tag question marker /-laN/
are homophonous. Only future tense tag-questions take a tense marker.
Sometimes, in negative tag-questions, /-ge/ replaces /-ye/ in the
future tense. |
| Example
- |
n
|
yśbi-ye
|
yśbi-ye/ge-ma-ne
?
|
|
you
|
will sleep,
|
won’t you?
|
|
|
| 4.15
Negative : |
The language
has two negative markers viz., /-ma/ and /-y /.
/-y /.
/-y / is negative
marker used for imperative sentences and /-ma/ is used elsewhere. / is negative
marker used for imperative sentences and /-ma/ is used elsewhere.
|
| 4.15.1.
Negative marker /-ma/ |
| (a)
To negate declarative sentence in present tense the tense marker
is optionally deleted and a negative marker is added. |
|
|
kin-ma
|
‘Ido no see’
|
|
I
|
see neg
|
|
|
bļ
|
g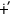 -t -t -ma -ma
|
‘He does not go’
|
|
he
|
go t neg
|
|
|
agergernėdė
|
ger-t( )-ma )-ma
|
‘The labourer does
not work’
|
|
labourer
|
do t neg
|
|
|
|
| However,
in embeded constructions, the deletion of tense marker is not permitted. |
  ager
ager |
ger kapė
|
mė-ma-dak
|
‘I do not intend
to work’
|
|
I work
|
do pp
|
thing neg t
|
|
bulu  N N
|
s gąp
kapė gąp
kapė
|
g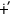 -mad -mad
|
‘They do jot go
to catch fish’
|
|
they fish
|
catch pp
|
go neg t
|
|
|
|
| 4.15.2
Past tense marker is optional when the sentence is negated. |
|
bė
|
islm
|
gér-(ka)-ma
|
‘He did not do this’
|
|
he
|
this
|
do t neg
|
|
|
bulu
|
yub-(ka)-ma
|
|
They did not sleep.
|
|
|
| 4.25.3.
Future Negative : |
| (i)
VR + Neg + ye |
| (ii)
VR + ye + Neg |