| /nįbra/ |
'father-in-law' |
/nįyąp/
|
'mother-in-law'
|
|
The
analysis of these forms would give the following morphemes.
|
/-na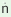 / / |
'cross cousin by marriage' |
| /-tya/ |
'second generation male' |
| /-ya/ |
'second generation female' |
| /-bą/ |
'first generation male' |
| /-mą/ |
'first generation female' |
| /-bra/ |
'first generation male(by
marriage)' |
| /-yąp/ |
'first generation female(by
marriage)' |
| /a-/ |
'male(with reference to ego)' |
| /jyi-/ |
female(with reference to
ego)' |
/nį-/
|
'parental relationship'
|
|
2.1.3.1.2.2.
|
Secondary Derived
Stems:
|
These are stems composed of at least one simple stem and one
derivative suffix.The constituent stem may belong to any class.
|
2.1.3.1.2.2.1.
|
Derivatives of Noun
Stems:
|
|
(i)
|
The derivative suffix
/-rć/ denotes ancestral relationship
beyond two generations.
|
| /nįya/ |
'grandmother' |
| /nayarć/ |
'female ancestor' |
| /nįtya/ |
'grandfather' |
/nįtyarć/
|
'male ancestor'
|
|
|
(ii)
|
The derivative suffix
/-ąk/ denotes colateral relations of parents with the relative
age difference marked obligatorily by the derivative suffixes
/-p/ and /-w/.
|
| /nįbą/ |
'father' |
| /nįbą-p-ąk/ |
'father's elder brother' |
| /nįbą-w-ąk/ |
'father's younger brother' |
| /nįmą/ |
'mother' |
| /nįmą-p-ąk/ |
'parent's elder sister' |
/nįmą-w-ąk/
|
'parent's younger sister'
|
|
The terms
for maternal uncle are different and do not follow this pattern
of derivation.
|
|
(iii)
|
The suffix /-ą/ derives
diminutives of the nouns to which it is attached.
|
| /tįra/ |
'dao' |
| /tįraą/ |
'knife' |
/p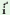 ya/ ya/ |
'bird' |
/p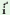 yaą/ yaą/
|
'robin'
|
|
2.1.3.1.2.2.3.
|
Derivatives of
Adjectival Stems:
|
The derivation is unmarked.The nouns are derived from adjectives
by a zero process(Ref.2.0.3).The adjectives represent abstract
qualities.
|
| /prą/ |
'good/goodness/virtue' |
| /maci/ |
'jealous/jealousy' |
| /masyį/ |
'secret/secrecy' |
/kįnįm/
|
'reason/reasonable'
|
|