a)
|
The R. dialect has the
plural allomorph -ri used exclusively with human masculine
nouns; --h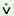 ,-´ga
used with human masculine and some neuter nouns the ,-´ga
used with human masculine and some neuter nouns the
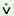 of
the plural suffix being the same as that of the fina 1 vowel of
the singular noun stem; -- ska ~ sika used with human feminine
nouns and some neuter nouns ; and --ka used exclusively with
neuter nonus. of
the plural suffix being the same as that of the fina 1 vowel of
the singular noun stem; -- ska ~ sika used with human feminine
nouns and some neuter nouns ; and --ka used exclusively with
neuter nonus.
|
b)
|
The L dialect has the
plural allomorph -ru and- ńga
occurring in the same environmental distribution as the R
dialect - ri and - ńga, -
ska occurring only with human fem. nouns and the same class of
neuter nouns as in the R. dialet but elsewhere it has -
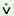
|
c)
|
The D dialect has only
- ńga
as the plural suffix
|
ii) Case
suffixes:
|
a)
|
The accusative case
suffix is - ?â in the R
dialect,
- ? ĩ in
the L and D dialeacts.
|
b)
|
The dative case suffix
is- ki in the R and L dia-
lects, - ?ĩ
in D dialects.
|
c)
|
The genitive case
suffix is - ti in the R and L
dialects, - ni in D dialect.
|
d)
|
The instrumental -
associative case suffix is - tole
in the R and L dialects - ŗe ? e
in D dialect.
|
|
iii) Pronouns
|
a)
|
The third person
masculine human singular pronouns have the forms evasi, e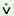 yu,
eva :nju in the R, L and D dialects respectively. yu,
eva :nju in the R, L and D dialects respectively.
|
b)
|
The third person
plural forms are evari in the R
dialect and evaru in the L and D dialects.
|
c)
|
The pronominal
suffixes for the 3rd person singular.
plu. respectively. are - esi : eri in the R dialect.
-é yu; - eru in the L. dialect and, -
enju : - eru in the D dialect.
|
| d)
|
The pronominal suffix
- ayi is used in the present
indicative with the 1st pers. plu. ind. in the R.
dial. while - o is used in the L dialect. |
The suffix - o is used to mark the optative of the verb in the
R. dialect as well as in the L dialect. |
| |