|
|
|
|
|
|
| (iii) |
I |
®
|
f |
/ |
{ i¾} |
|
|
|
|
|
{ ¾i
}
|
|
|
Lower high /I/ is dropped in the environment of high vowel/i/. Examples
are:
|
|
pi-Iye
|
®
piye
|
‘(please) drink’ (IIp.sg. imp.)
|
|
pi-Iyo
|
®
piyo
|
‘(please) drink’ (IIp.pl. imp.)
|
|
kI-y-i
|
®
kI-f-i-ki
|
‘did’ (fem.sg.)
|
|
lI-y-i
|
®lI-f-i-li
|
‘took’(fem.sg.)
|
|
|
(iv)
 ®e/¾y ®e/¾y
|
|
|
The stem final vowel /- /
becomes /-e/ beofe /-y-/ participal suffix. Examples are : /
becomes /-e/ beofe /-y-/ participal suffix. Examples are :
|
|
g -y-o
® -y-o
®
|
geyo
|
‘went’(mas.sg.)
|
|
k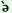 -y-o
® -y-o
®
|
kéyo
|
‘said’(mas.sg.)
|
|
r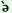 -y-o
® -y-o
®
|
réyo
|
‘lived’(mas.sg.)
|
|
l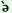 -y-o
® -y-o
®
|
léyo
|
‘fell’(mas.sg.)
|
|
|
Where as :
|
|
pè-y-o
®
|
pèyo
|
‘made wet’(mas.sg.)
|
|
pè-y-i
®
|
pèi
|
‘made wet’(fem.sg.)
|
g
 -y-i
® -y-i
®
|
g
 i i |
‘went’(fem.sg.) |
|
|
(v) The final vowel /
 /
of the verbal roots becomes /€/
before infinitive suffix / /
of the verbal roots becomes /€/
before infinitive suffix /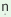 /
and participle suffix /t/. /
and participle suffix /t/.
|
|
Examples:
|
|
r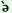 - - -o ® -o ®
|
r  o o
|
‘to lve’
|
|
r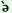 -t-o
® -t-o
®
|
r to to
|
‘living’
|
|
k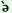 - - -o
® -o
®
|
k  o o
|
‘to say’
|
|
k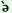 -t-o
® -t-o
®
|
k to to
|
‘saying’
|
|
l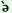 -t-o
® -t-o
®
|
l to to
|
‘falling’
|
l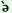 - - -o
® -o
®
|
l  o o
|
‘to fall’
|
|
|
(vi) All the vowels of the CV(C) or CVCX transitive as well as
intransitive root stems when followed by derivative suffixes such as {-ai}
an abstract noun formative and {-a}, {-wa} etc. causative suffixes, change
to /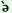 /
Examples are: /
Examples are:
|
|
|
|
(vii) Final vowels /i/, /u/ of disyllabic stems when followed by
inflection suffixes become /I/ and /U/ respectively. A few examples are :
|