|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 ssi ssi
|
‘eighty’ as in
|
 ssi
kò ssi
kò a a
|
‘eighty horses’
|
|
-asi
|
as in
|
 n-asi n-asi
|
‘eighty nine’
|
|
|
Ik-asi
|
‘eighty one’ |
|
|
trIy-asi
|
‘eighty three’ |
|
|
c r-asi r-asi
|
‘eighty four’
|
|
|
p c-asi c-asi
|
‘eighty five’ |
|
|
chIy-asi
|
‘eighty six’ |
|
|
s t-asi t-asi
|
‘eighty seven’
|
|
|
 ţh-asi ţh-asi
|
‘eighty eight’
|
|
-si
|
as in
|
basi
|
‘eighty two’ |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
n bb€ bb€
|
‘ninety’
|
as in
|
|
|
|
|
n bb€ bb€
|
r p p ya ya
|
‘ninety rupees’
|
|
anm€
|
|
as in
|
 nanm€ nanm€
|
‘eighty nine’
|
|
Ik-anm€
|
|
‘ninety one’
|
|
|
|
banm€
|
|
‘ninety two’
|
|
|
|
tIranm€
|
|
‘ninety three’
|
|
|
|
c ranm€ ranm€
|
|
‘ninety four’
|
|
|
|
pIcanm€
|
|
‘ninety five’
|
|
|
|
c hyanm€
|
|
‘ninety six’
|
|
|
|
s tanm€ tanm€
|
|
‘ninety seven’
|
|
|
|
 ţhanm€ ţhanm€
|
|
‘ninety eight’
|
|
|
|
Inm€
|
|
as in |
n  Inm€ Inm€
|
‘ninety nine’
|
|
|
Inflexion of Cardinal Numerals :
|
|
All the numerals have two forms one direct as described above and the
other oblique occurring before postpositions. All the cardinals except /ek/
‘one’ are inflected for plural and in some cases the shape of the
direct form changes in the oblique form. In oblique /ek/ takes {- 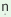 }
suffix as }
suffix as
|
|
/ek 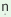 i n€ kIyo/ ‘Only one did’ and all the others take
{-ã}
suffix in oblique like other nominals.
i n€ kIyo/ ‘Only one did’ and all the others take
{-ã}
suffix in oblique like other nominals.
|
| |
|
Examples are :
|
|
Direct
|
Oblique |
|
do
|
dowã
|
|
tr€
|
trUwã
|
|
car
|
c Uwã Uwã
|
|
p nj nj
|
p njã njã
|
|
che
|
c eyã eyã
|
|
s t t
|
s ttã ttã
|
|
 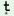 h h
|
 ţtţhã ţtţhã
|
|
n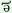 u u
|
n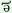 Uwã Uwã
|
|
d s s
|
d sã sã
|
|
|
|
|
Another alternative way of counting numbers is found in the language
mostly used by the illiterate people and is used to count above twenty.
This is the way of counting by twenties and the multiplied digit is put
preceding {bí}
‘twenty’ such as :
|