4.
|
MORPHOLOGY
|
4.1.
|
Noun
|
Nouns in Bhumij may be classified broadly into two : simple
nouns and derived nouns.The simple nouns may be further classifie dinto
animate nouns and inanimate noun. There are some exceptions in the
classification of animate and inanimate nouns. For example, ‘Sun’ and ‘Moon’
are classified as animate nouns.
|
4.1.1.
|
Simple Nouns
|
4.1.1.1.
|
Animate Nouns
|
h 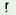 
|
‘man’ |
ku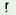 ihon ihon
|
‘woman’ |
u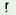 i? i?
|
‘cow’ |
| seta |
‘dog’ |
sad m m
|
‘horse’ |
| pusi |
‘cat’ |
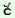 e¸e e¸e
|
‘bird’ |
bi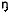
|
‘snake’ |
| merom |
‘goat’ |
| hon |
‘child’ |
|
4.1.1.2.
|
Inanimate nouns
|
| daru |
‘tree’ |
| baba |
‘paddy crop’ |
 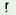 a a
|
‘house’ |
b i i
|
‘book’ |
ma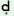 ·i ·i
|
‘cooked rice’ |
ga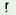 a a |
‘river’ |
| duar |
‘door’ |
| datrum |
‘sickle’ |
| madal |
‘apple’ |
| diri |
‘stone’ |
jo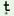 a a
|
‘fruit’ |
| sono |
‘shirt’ |
| buru |
‘mountain’ |
|
4.1.2.
|
Derived Nouns
|
The derived nouns may be classified into four on the basis
of their derivational process.
|
1.
|
Nouns which are derived by prefixing the first syllable
of the verbs to the verbs.
|
2.
|
Nouns which are derived by suffixing
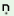 i? or ji? to the verbs. i? or ji? to the verbs.
|
3.
|
Nouns which are derived by suffixing
i? to the verbs with
tense markers.
|
4.
|
Nouns which are derived by suffixing
-i, -a or ni with
the adjectives.
|
The nouns
which are formed by prefixation are action nouns like ‘eating’,
‘drinking’ etc. The nouns which are formed by suffixation
with the suffixes
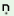 i?
/ ji? are agentive nouns which refer to the doer of the action
like ‘eater’, ‘drinker’ etc. The nouns which are
derived from the verbs with tense markers are agentive nouns
giving the time of the action like ‘one who is doing the
action’, ‘one who did the action’ etc. i?
/ ji? are agentive nouns which refer to the doer of the action
like ‘eater’, ‘drinker’ etc. The nouns which are
derived from the verbs with tense markers are agentive nouns
giving the time of the action like ‘one who is doing the
action’, ‘one who did the action’ etc.
|