| ?th- |
olta?th 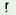  |
‘author’ |
-mp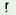 - -
|
pamp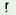 ai ai |
‘butterfly’ |
|
4.
|
Final two consonant clusters :
|
| -?p |
hap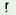 u?p u?p |
‘to embrace’ |
| -?t |
puttri?t |
‘foam’ |
| -nt |
ka:nt |
‘wall’ |
|
2.6.
|
Syllable
|
There may be many ways for the syllabic cut.
However, it could be done by observing the way the native speaker
pronounces the words. Further, there is a natural tendency of syllabic cut,
based on the human vocal mechanism. There may be the combination of words.
For example, lelke-daiŋ is the
combination of three morphemes. So, the syllabic cut can be made as
lel-ked-aiŋ rather than some other way.
The word aiŋ is a single morpheme with
vowel clusters. So, this could be treated as a single syllable. The same way
the word hai may be considered.
|
The word jilu akhriŋh 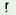  ‘butcher’ may be syllabified as ji-lua-khriŋ-h
‘butcher’ may be syllabified as ji-lua-khriŋ-h - -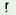  but this may not be correct because jilu is a word, akhriN
is another word and h
but this may not be correct because jilu is a word, akhriN
is another word and h 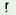  is another word. So, it is better to divide as ji-lu-akh-riŋ
h
is another word. So, it is better to divide as ji-lu-akh-riŋ
h - -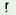  rather than the other way.
rather than the other way.
|
|
The sequence of phonemes with a single peak sonority is a
syllable. There may be one or more syllables ina word. In each syllable, the
vowel is the peak of sonority, and is called the nucleus of the syllable.
The nucleus may be preceded and followed by one or more consonants. The
preceding consonants are called onset of the syllable and the following
consonants are called coda of the syllable. If the syllable ends in a vowel,
it is called as open syllable and if it ends in a consonant, it is called a
closed syllable.
|
The words in Bhumij consist of one to six syllables, though
the word with two syllables are common. The following are the different
syllabic patterns of Bhumij.
|
2.6.1.
|
Monosyllabic words :
|
| a. open syllable: |
c v (v) |
|
|
| c v |
ti |
‘hand’ |
| c v v hai ‘fish’ |
|
|
|
| b. closed syllable |
(c) (c) |
(v) vc (c) |
|
|
| vc |
il |
‘feather’ |
| vvc |
aiŋ |
‘I’ |
| cvs |
hon |
‘child’ |
| ccvc |
swan |
‘to smell’ |
| vcc |
’u?l |
‘mushroom’ |
| cvcc |
ka:nt |
‘wall’ |
|
2.6.2.
|
Disyllabic words :
|
a. second syllable is open
|
(c) v (v) (c) |
- (c) cv (v) |
|
| v-cv |
aba |
‘father’ |
| cv-cv |
haga |
‘brother’ |
| vc-cv |
ekla |
‘to shiver’ |
| cvc-cv |
dalki |
‘swamp’ |
| cvv-cv |
piaji |
‘onion’ |
| cvc-ccvv |
pamp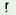 ai ai
|
‘butterfly’ |
|
b. second syllable is
closed : -
|
(c) (c) v (c) |
cvc (c) |
|
| v-cvc |
ačar
|
‘pickle’ |
| vc-cvc |
iskul |
‘school’ |
| cvc-cvc |
datrum |
‘sickle’ |
| ccv-cvc |
srab n n
|
‘name of month (Jul-ug.)’ |
| cvc-cvcc
|
hap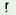 u?p u?p |
‘to embrace’
|
|