| 7.8.11.1. Past Durative |
|
The past durative is formed by adding the durative suffix to the past stem of the verb.
|
| Examples: |
|
tit-inton-a:n |
‘I was eating’ |
|
tit-intor-o:r |
‘they were eating’ |
|
tit-intor-u: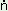 |
‘they (non-masc.) were eating’ |
|
tit-inton-i:r |
‘you(pl.)were eating’ |
|
| 7.8.11.2. Future Durative |
|
The future durative is formed by adding the durative suffix to the future stem of the verb.
|
| Examples: |
|
ke:njk-inton-a:n |
‘I will be listening’ |
|
ke:njk-intor-o:m |
‘we will be listening’ |
|
wa:yk-inton-i:n |
‘you (sg.) will be coming’ |
|
wa:yk-intor-i:r |
‘you (pl.) will be coming’ |
|
wa:ya:r-inton-a: |
‘it will be coming’ |
|
|
The durative suffix is followed by the personal pronominal endings (Set-6).
|
| Persons |
Singular |
Plural |
| I |
a:n |
-o:m |
| II |
-i:/-i:n |
-i:/-i:r/i: |
| III Masculine |
-o:r |
o:r |
| III Non-masc. |
-a |
u: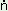 |
|
| 7.8.12. Perfective |
|
Perfetive aspect is of two kinds:
|
| (i) Past perfective and |
| (ii) Imperfective. |
|