| |
|
|
|
However, this present tense marker is not added to the verb /ali/
‘be’. Only /e /,
the habitual aspect marker, is added to this verb. In other
words, there is no contrast between simple present and habitual
with the ‘be’ verb. /,
the habitual aspect marker, is added to this verb. In other
words, there is no contrast between simple present and habitual
with the ‘be’ verb. |
|
|
|
4.3.3. The Future : |
| |
The future
tense marker is /c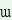 /. /. |
| |
pá
a u-c u-c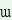 ‘he will come’
‘he will come’ |
pa nok campí-c nok campí-c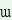 ‘they will speak’
‘they will speak’ |
ní
àwa-c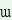 ‘I will swim’
‘I will swim’ |
| |
| 4.4.
Aspects : |
| |
| There are
four aspects in Ao, viz., habitual, durative, perfect and
immediate. Some of them are restricted to one or two particular
tenses, as discussed below. |
| |
The habitual
marker is /-e /
and it has a phonological variant /- /
and it has a phonological variant /- /,
which occurs with verbs ending in vowels /a, u, o/. /,
which occurs with verbs ending in vowels /a, u, o/. |
| |
pá
pala- ‘he divorces’
‘he divorces’ |
ní
a u- u- ‘I come’
‘I come’ |
lá
awó- ‘she goes’
‘she goes’ |
| |
/-e /
occurs with verbs ending in consonants and other vowels. When it
occurs after vowels, the glide /y/ is inserted. /
occurs with verbs ending in consonants and other vowels. When it
occurs after vowels, the glide /y/ is inserted. |
| |
ní acem-e ‘I drink’
‘I drink’ |
ná ani-y-e ‘you lead’
‘you lead’ |
lá
an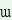 -y-e -y-e ‘she paints’
‘she paints’ |
| |
| The durative
aspect occurs with past and future tenses. That is, there is no
distinction between simple present and present durative. The
markers are /a/ and /i/, which occur with the positive verb and
with the negative verb respectively. This aspect marker is added
to the verb root and is followed by the past and future of verb
/ali/ ‘be’. |
| |
| ní cem-a liyasm
‘I was drinking’ |
ní cem-a alic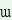 ‘I will be drinking’
‘I will be drinking’ |
ní
me-cem-i liyas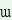 ‘I was not drinking’
‘I was not drinking’ |
ní
me-cem-i alic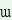 ‘I will not be drinking’
‘I will not be drinking’ |
| |
| The perfect
aspect marker /uko/ or /oko/ and it occurs only in the past. /uko/
and /oko/ are in free variation (note that the classificatory
prefix /a/ is dropped since this marker begins with a vowel). |
| |
|
acem
cem-uko ~
cem-oko
‘had drunk’ |
azu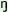 zu
zu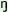 -uko
~ zu -uko
~ zu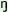 -oko
‘had read’ -oko
‘had read’ |
|
aci
ci-uko
~
ci-oko
‘had ate’ |
| |
| The
immediate aspect marker is /-li/ and it occurs with all three
tenses. |
| |
cem-li
liyas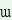 ‘just drink’
‘just drink’ |
cem-li
liye ‘is just drinking’
‘is just drinking’ |
cem-li
alic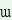 ‘will just drink’
‘will just drink’ |
| |
| 4.5.
Imperative : |
| |
The
imperative suffix is /a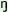 /
and it has a phonologically conditioned variant /- /
and it has a phonologically conditioned variant /-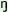 /. /. |
| |
/-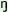 /
occurs with verbs ending in vowels except /i/ and / /
occurs with verbs ending in vowels except /i/ and /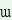 /
: /
: |
| |
a u- u-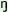 ‘come !’
‘come !’ |
aka-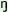 ‘shoot !’
‘shoot !’ |
ata-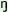 ‘wait !’
‘wait !’ |
sò o- o-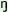 ‘cook !’
‘cook !’ |
a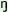 ó- ó-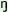 ‘see !’
‘see !’ |
z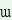 lu- lu-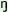 ‘write down !’
‘write down !’ |
| |